A seismic shift in geoeconomics is currently underway as the pace of economic fragmentation accelerates worldwide. For small businesses, a domestic megaregion or international approach may be prudent as the risk of business survival increases. Trump 2.0 and its economic policy driven by tariffs are set to reshape the global landscape for years to come. The shift while creating enormous near-term uncertainty presents numerous opportunities for today’s small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, the path to global success is filled with minefields made even more challenging in today’s fluid and evolving economic environment. To grow and thrive, SMEs must adapt, focus on building new partnerships, and develop creative strategies for market expansion.
This blog post explores opportunities and challenges for SMEs when expanding globally. We discuss standard approaches to global expansion and potential pitfalls to avoid. We’ll delve into the advantages of the Employer of Record (EOR) to test new markets or accelerate market entry and what factors SMEs should consider when selecting an EOR provider. Finally, we’ll highlight Deel’s EOR services and demonstrate how they can empower SMEs to compete effectively in the global marketplace. We’ll offer various use cases to demonstrate the value of the EOR model as part of international expansion strategies. Be sure to follow us on LinkedIn. Now let’s get started.
Tariffs and Trump 2.0
The new tariffs imposed during Trump 2.0 continue to influence the global trade landscape in 2025. We expect the impact to be long-lasting. On March 25, 2025, the administration announced a 25% tariff on all imported vehicles entering the US. Additional tariffs across a range of industries are set to take effect on April 2, 2025. The focus is primarily on the 15% of trading partners that maintain trade imbalances with the United States. These countries include Indonesia, Canada, the EU, South Korea, Japan, etc. Whatever the outcome, what’s clear is that businesses are most likely to face increased costs and supply chain complexities, necessitating adaptive strategies. The emphasis on trade resilience and diversification, accelerated by these tariffs, has led to increased interest in regional trade agreements and alternative sourcing strategies, shaping how SMEs approach international expansion.
Opportunities for Global Expansion
Despite increasing volatility in global economic activity, the global marketplace presents many opportunities for ambitious SMEs. In just the last 6 months, the global economic landscape shifted from expectations of robust growth to contraction. Moreover, rapid innovation and the impact of artificial intelligence continue to create labor market upheaval, reshaping the future of work. However, competitive barriers continue to fall as AI becomes more ubiquitous
Today even solopreneurs and small businesses can tap new international markets once the exclusive purview of large corporations. These new opportunities span various dimensions, from accessing new customer segments to leveraging global talent pools and optimizing operational costs. By strategically navigating these global dynamics, SMEs can drive significant growth and build resilience through diversification.
Despite the volatility, international expansion offers advantages to forward-thinking small and medium-sized enterprises. Let’s dive into these core reasons.
Access to New Markets and Customers
There are numerous opportunities for small businesses to expand in the $105 trillion global economy. One of the primary advantages is access to new markets and customers. Entering new countries allows SMEs to tap into previously unreached demographics, potentially increasing their customer base exponentially. This expansion can lead to significant revenue growth and help businesses diversify their income streams, reducing reliance on a single market.
In the increasingly volatile global economy, regional trade blocs such as RCEP and the EU will benefit. The economic impact of the US tariff policy likely will force a realignment of these regional trading bloc relationships. However, advantages under the USMCA will likely diminish as economic partnerships unravel and upcoming negotiations become strained. Moreover, nearshoring and friendshoring once reliable strategies to manage supply chain risk, are now in doubt given diminishing visibility in geopolitical alliances impacting supply chain resilience. For markets such as the US, reshoring will emerge as the primary model for market access in the near to medium term.
Access to Global Talent
Additionally, global expansion often provides access to new talent pools. In today’s knowledge-based economy, hiring skilled workers worldwide give SMEs a competitive edge, allowing them to innovate and adapt quickly to changing market conditions. There are over 500 million knowledge workers in Asia alone, providing ample opportunities for companies to tap a global talent pool to address workforce issues in their home market or strengthen the required talent pool when expanding internationally. Remote and distributed workforces are growing in importance, with companies like Deel developing various solutions to optimize and streamline global workforce management for clients worldwide.
Cost Reduction and Optimization
Another opportunity lies in the potential for cost reduction. Some countries may offer lower operational costs regarding labor, raw materials, or overheads. By strategically expanding into these markets, SMEs can optimize their cost structure, better manage their supply chains, and improve profitability. Additional advantages of owning your supply chain include:
- Enhanced Control: By owning your supply chain, you have direct control over production, quality, and delivery. This can help ensure that products meet your exact specifications and are delivered on time.
- Reduced Costs: While initial investments might be necessary, owning your supply chain can lead to long-term cost savings. You can optimize production processes, negotiate better supplier deals, and avoid intermediaries’ fees.
- Improved Brand Protection: Direct control over your supply chain can help safeguard your brand’s reputation. You can monitor production conditions, ensure ethical practices are followed, and prevent counterfeit products from entering the market.
- Increased Market Flexibility: Owning your supply chain can give you greater flexibility to respond to market changes. For example, you can quickly adjust production levels to meet increased demand or modify product designs to cater to local preferences.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Owning your supply chain can better protect your intellectual property. You can control the manufacturing process and prevent unauthorized access to your proprietary information.

Innovation and Learning
Furthermore, international expansion can provide valuable learning experiences and foster innovation. Exposure to different business practices, consumer preferences, and cultural norms can spark new ideas and drive product or service improvements that benefit the company globally. Demand growth for consumer products across Asia and Africa continues to drive interest in e-commerce, fintech, and other innovative solutions to address the needs of a young and rapidly expanding middle class.
Challenges of Global Expansion
Many SMEs offer compelling products and services for a global audience. While international markets may appear appealing, SMEs venturing beyond their borders face many complex challenges. We do recommend staying closer to home. The breadth and depth of the $26 trillion US economy provide multiple megaregions on par with the GDP of many European and Asian countries. Obstacles to international expansion can be formidable, potentially derailing even the most promising expansion plans if not carefully navigated. From complex regulatory landscapes to cultural nuances and financial investment, the path to global success is fraught with potential pitfalls. Understanding these challenges is crucial for SMEs, in order to develop robust strategies and seek appropriate support, such as EOR services, to mitigate risks and maximize their chances of international success.
Regulatory Complexities
However, alongside these opportunities come significant challenges. One of the most daunting obstacles for SMEs’ international expansion is navigating the complex regulatory environments of different countries. Each nation has its own set of laws governing business operations, employment, taxation, and data protection, among other areas. Certain markets such as the United States and the US tend to be regulation-heavy. As such, compliance with these regulations can be time-consuming and costly, particularly for small businesses with limited resources.
Cultural and Language Barriers
Language barriers and cultural differences can also pose significant challenges, affecting everything from marketing strategies to day-to-day operations and employee management. Hiring or partnering with local players can help overcome some of these challenges.
Financial Hurdles
Financial hurdles are another primary concern for SMEs looking to expand globally. International expansion often requires substantial upfront investment, whether establishing local entities, hiring staff, or adapting products and services for new markets. Currency fluctuations and international banking complexities can further complicate financial management.
Competitive Landscape
Large multinational corporations or local players hold the edge when competing to gain a foothold in new international markets. Understanding these competitive dynamics is an essential part of developing the right market entry strategy. However, the level of competitive intensity is usually sector-dependent.
Common Approaches to International Expansion
Given these challenges, SMES must approach international expansion strategically. Generally, multinational corporations have a competitive edge in terms of human and financial resources. Local players have the edge in terms of market knowledge and relationships. As such, SMEs need to move cautiously when expanding internationally. In today’s global business landscape, multiple strategies exist for SMEs to enter new markets and build a thriving global business. Certain strategies are more suited to certain types of companies depending on the sector or product and services offered. When considering international expansion, the following core strategies are usually deployed.
Establishing Local Subsidiaries
One traditional method is establishing a local subsidiary or branch office in the target country. This approach gives the company full control over its operations but requires significant investment and a deep understanding of local regulations. In recent years, countries across the Middle East and ASEAN have relaxed foreign ownership rules. Now, foreign companies can own 100% of local entities. However, ownership remains limited to specific sectors and levels of paid-up capital.
Partnerships and Joint Ventures
Another approach is to enter into partnerships or joint ventures with local businesses. JVs and partnerships can provide valuable local knowledge and resources but may require sharing control, profits, and IP. Given the need to build relationships, partnership selection can be time-consuming and costly for smaller organizations. Also, partnership failure can be expensive regarding market exit or the need to find new partners.
Franchising
Franchising is another popular expansion strategy, particularly in the retail and food service industries. The franchise model allows SMEs to expand rapidly with lower capital investment but choosing the right franchisees can mean the difference between success and failure. Additionally, ongoing support is required to maintain brand consistency. The global franchising industry is expected to grow at a 9.75% CAGR between 2021 and 2032 to reach $279 billion. Other industries well suited to franchising include:
- Automotive repairs and services
- Environmental services
- Hair salons
- Health aids and services
- Computer and phone repair
- Clothing stores
- Children’s services
E-commerce and Digital Platforms
E-commerce and digital platforms have also opened up new avenues for international expansion, allowing businesses to reach global customers without establishing a physical presence in foreign markets. Companies such as Amazon, Lazada, and Temu have contributed to an e-commerce market valued at nearly $19 trillion in 2022. Growing at a 12.22% CAGR from 2022, the market is expected to reach $47 trillion by 2030. Additionally, SaaS models offer a resource-light model to expand internationally. The SaaS market is currently valued in excess of $2 trillion and is expected to reach $10 trillion by 2030. While digital platforms tend to be asset lite, effective engagement with an online customer base is key to success.

Common Pitfalls in International Expansion
Although the benefits of international expansion are clear, many companies fail in their attempts to expand internationally. Reasons vary with common pitfalls that include:
Inadequate Market Research
One common reason for failure is inadequate market research. SMEs may overestimate their product or service demand in a new market or need help understanding local consumer preferences and behaviors. Companies may chase the hype of a particular region with a “we need to be there” attitude. Alternatively, they may rush to a new market due to challenges in other international markets. Before expanding internationally, companies must conduct proper due diligence and carefully weigh the pros and cons. Due diligence should also include exploring options in your domestic market prior to expanding internationally. Fortunately, significant resources are available to help companies climb the learning curve and understand the risks of a new market.
Underestimating Resource Requirements
Another pitfall is underestimating the resources required for successful expansion. International growth often requires significant time, money, and personnel, and SMEs that stretch themselves too thin may need help to maintain quality and service levels. This underestimation remains a crucial weakness compared to multinationals, which have the resources (capital and human) to expend or write off when entering a new market.
Cultural Missteps
Cultural missteps can also lead to failure. Companies that don’t adapt their products, services, or marketing strategies to local tastes and customs may struggle to gain traction. This is an issue with both large and small businesses. Walmart’s failure in South Korea and Carrefour’s exit from Asia highlight some of the challenges even large companies face when expanding internationally. Research, resources, and relationships are important in mitigating these risks.
Regulatory Non-Compliance
Similarly, failing to understand and comply with local regulations can result in legal issues, fines, or even forced market exit. In highly regulated markets such as the EU or the United States, the cost of compliance remains high. For example, in the United States home health aids, construction workers, call center workers, and truck drivers constantly face a risk for misclassification. Monetary penalties range from $1,000 to $10,000 per violation.

The Employer of Record (EOR) Model
Given these challenges, many SMEs are turning to the Employer of Record (EOR) model as a strategy for international expansion. An EOR is a third-party organization that takes on the legal responsibility of employing staff in a foreign country on behalf of another company. It allows you to hire full-time employees without having to set up a legal entity in a new country.
When to Use and EOR
The EOR strategy is not for everyone. For companies seeking to hire internationally, an EOR is an option if:
- Companies can’t afford to register local entities in order to hire globally
- Don’t have the internal expertise or are worried about the cost to ensure compliant contracts
- Need to enter quickly enter new markets, quickly and rapidly onboard employees
- Want to offer employees multiple benefits and perks
Benefits of an EOR Model
Simplified Compliance
First and foremost, using an EOR can dramatically simplify compliance with local employment laws and regulations. The EOR is responsible for ensuring that all employment practices, from hiring to termination, are compliant with local laws. Common employment activities include managing payroll, taxes, benefits, and other HR-related tasks.
Faster Market Entry
The EOR model also allows for much faster market entry. Instead of spending months or even years setting up a local entity, SMEs can start operating in a new country within weeks. This agility can be a significant competitive advantage, allowing businesses to respond quickly to new opportunities or changing market conditions.
Financial Flexibility
Financial flexibility is another key benefit of the EOR model. SMEs can significantly reduce the upfront costs of international expansion by eliminating the need to establish a local entity. The EOR model also provides more flexibility in terms of workforce management. Companies can more easily scale their operations up or down in response to business needs without the complexities of direct hiring and layoffs in a foreign country. It’s an excellent option if testing a new market or onboarding a remote workforce with particular skills.
Selecting EOR Providers
When selecting an EOR provider, SMEs should consider several factors. The list of factors for an EOR provider includes
- Geographic Coverage: The provider’s geographic coverage is crucial – they should have a strong presence in the target markets for expansion.
- Range of Services: The range of services offered is also important. While payroll and compliance are standard, some EORs provide additional services such as recruitment support, benefits administration, or strategic HR consulting.
- Technology Platform: Another key consideration is the technology platform used by the EOR. A robust, user-friendly system can greatly simplify the management of international employees.
- Track Record and Reputation: SMEs should also examine the EOR’s track record and reputation. References from other clients, particularly those of similar size or in similar industries, can provide valuable insights.
- Cost and Value: Cost is naturally a factor, but it’s essential to consider the total value provided rather than just the base price. A slightly more expensive EOR that offers superior compliance expertise or better technology may provide better value in the long run.
- Support Level: SMEs should consider the level of support the EOR provides. Responsive, knowledgeable customer service can be invaluable when navigating the complexities of international employment.
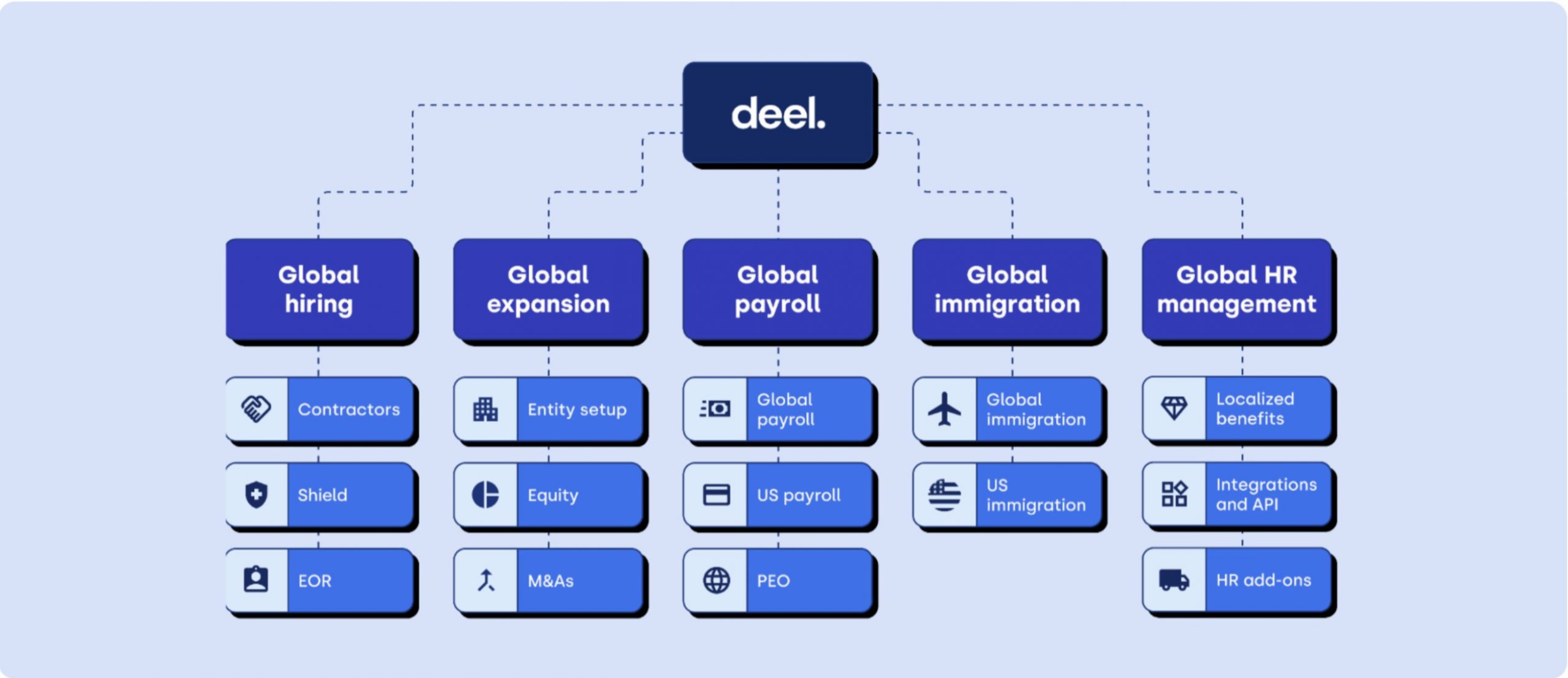
Deel’s EOR Services
One EOR provider that has gained significant attention in recent years is Deel. In just a few years, Deel has become one of the world’s leading global workforce solutions companies, offering a comprehensive suite of services for HR, payroll, immigration, and compliance. The company provides a comprehensive EOR solution to simplify global hiring and compliance for businesses of all sizes. Deel’s EOR services cover over 90 countries, making it a versatile choice for SMEs with ambitious international expansion plans.
Competitive Advantages of Deel’s EOR Services
Comprehensive Employment Management
One key advantage of Deel’s EOR services is their end-to-end approach to international employment. They handle the entire local employment process, from onboarding and payroll to benefits administration and offboarding. Additionally, Deel clients get exclusive access to their talent market, with access to the top 3% of global talent. This comprehensive service allows SMEs to focus on their core business activities while Deel manages the complexities of international employment.
User-Friendly Platform
Deel’s platform is user-friendly and efficient. Clients can set up new hires quickly, with Deel handling all the necessary paperwork and compliance checks. The platform also offers features like mass invoice approvals and easy access to digital invoices and receipts, simplifying financial management for SMEs operating across multiple countries.
Deel Mobile
Deel recently launched its mobile app to meet the needs of both their clients and workers wherever they are in the world. The app allows users to
- Personalize your workspace: Ad widgets for quick access to your most used features, such as Deel AI, recent payments, and the Compliance Hub
- Easily switch between core products and services: Users can easily access services such as Engage, Payroll, and their resource hub with streamlined navigation.
- Rapid discovery of services: Users benefit from improved discoverability, which reduces search time and increases productivity.
Deel Mobile Dashboard
Robust Compliance Management
One particularly noteworthy aspect of Deel’s service is their attention to compliance. They ensure that all employment practices comply with local laws, including mandatory benefits, social security contributions, and tax withholdings. This level of compliance management can be invaluable for SMEs that may not have the resources to navigate the complexities of international labor laws on their own. Deel also offers a misclassification guarantee to cover the risk of contractor or employee misclassification.
Flexible Compensation Structures
Deel also offers flexibility in terms of compensation structures. Their platform supports various types of payments, including salaries, bonuses, commissions, and expense reimbursements. They even facilitate payment in crypto (Bitcoin, Ethereum, USDC, Dash, Solana, and BUSD), which can be a powerful tool for attracting and retaining top talent.
Comprehensive Employee Management Tools
Another advantage of Deel’s service is its support for ongoing employee management. They provide tools for tracking paid time off, managing performance bonuses, and handling other employee lifecycle aspects. This comprehensive approach can help SMEs provide a consistent employee experience across all their international operations.
Additional Benefits Options
Deel’s service also includes access to additional benefits options, such as private health insurance and pension offerings. These services can help SMEs create competitive compensation packages to attract top talent in international markets.

Insights and Information From Deel
To better understand the EOR process including challenges and pitfalls we’ve put together a list of resources to guide you through the journey. Follow the links below to learn more.
EOR and Global Hiring Resources
- Everything EOR: A Guide to Employer of Record
- Employer of Record Services for Enterprises
- US Company Guide to Hiring Foreign Independent Contractors
- A Complete Guide to Contractor Management for Global Businesses
Use Cases: How EOR Services Help SMEs
To illustrate how an EOR service like Deel can help SMEs, let’s consider three use cases:
Case 1: Accessing International Talent
First, imagine a small software company based in the United States that wants to hire a talented developer they’ve found in Germany. Without an EOR, the company would need to establish a legal entity in Germany, understand and comply with German employment law, set up a local payroll system, and manage benefits according to complex German and EU standards. This process could take months and cost tens of thousands of dollars. With an EOR like Deel, the company could hire the developer within days, with Deel handling all the legal and administrative aspects of employment. Using an EOR allows US small businesses to access international talent quickly and cost-effectively, giving them a competitive edge in the fast-moving tech industry.
Case 2: Expanding Customer Service Globally
In our second use case, consider a growing e-commerce business based in the UK that wants to expand its customer service team to cover more time zones. They’ve identified potential team members in the Philippines and Brazil but remained concerned about the prospect of complying with employment laws in these countries. Using an EOR service, the company can quickly establish a presence in both countries without needing local entities. The EOR handles payroll in local currencies, ensures compliance with local labor laws, and manages mandatory benefits. Using an EOR allows the e-commerce business to provide 24/7 customer service, improve customer experience, and potentially drive sales growth.
Case 3: Testing New Markets
For our final use case, let’s look at a manufacturing SME based in Canada that wants to set up a sales office in India to tap into the growing market there. Traditionally, this would involve a significant investment in establishing a local entity, hiring local legal and accounting support, and navigating the complexities of Indian business regulations. With an EOR service, the company can hire local sales staff quickly and compliantly without needing a local entity. The EOR handles all aspects of employment, from contracts to payroll to termination, if necessary. The EOR allows the manufacturing SME to test the market with minimal upfront investment and risk, providing the flexibility to scale up or down based on their success in the new market.
Enhancing Competitiveness: SME Global Expansion with EOR Services
In conclusion, while global expansion offers significant opportunities for SMEs, it also presents considerable challenges. The complexities of international employment law, the costs of establishing local entities, and the risks of non-compliance can be prohibitive. However, the EOR model, as exemplified by services like Deel, offers a solution that can help SMEs overcome these hurdles. By handling the legal and administrative aspects of international employment, EORs allow SMEs to focus on their core business activities while expanding into new markets quickly and compliantly. Whether accessing international talent, providing global customer service, or testing new markets, EOR services can give SMEs the agility and support they need to compete effectively in the global marketplace. As global competition heats up and the workforce becomes more remote EOR services will likely play an increasingly important role in enabling SMEs to realize their global ambitions.
To learn more about EOR services from Deel reach out to the ClearSky 2100 Ventures team or visit Deel to sign up for a free demo.
Disclosure: At ClearSky 2100, our portfolio partly consists of affiliate partnerships. We may earn a small commission from buying links on our site at no cost to you.