Leadership paradigms in the business world constantly evolve, with organizations seeking models that drive success while nurturing a positive workplace culture. Among these approaches, servant leadership has emerged as a powerful philosophy, gaining significant traction in recent years. This innovative concept turns the traditional top-down hierarchy on its head, emphasizing the leader’s role in serving and empowering team members. Servant leadership represents a radical departure from conventional management styles, prioritizing the growth and well-being of employees and the communities they serve. On its face, it may appear dissonant in a cutthroat global business environment. Nevertheless, this approach aims to create more engaged, innovative, and purpose-driven organizations by fostering a culture of support, collaboration, and shared purpose.
This blog post explores servant-leadership’s origins, principles, and impact. We compare the servant model to other leadership styles. We’ll also look at how this model reshapes modern organizational dynamics and why many successful companies embrace its tenets. Be sure to follow us on LinkedIn. Now let’s dive in.
The Origins of Servant Leadership
Robert K. Greenleaf first introduced the concept of servant leadership in his 1970 essay “The Servant as Leader.” Drawing inspiration from Hermann Hesse’s novel Journey to the East, Greenleaf proposed a leadership model in which the leader’s primary goal is to serve others. At the time, this servant leadership approach marked a radical departure from traditional command-and-control leadership styles.
Greenleaf defined a servant-leader as someone who begins with the natural feeling that one wants to serve first. This conscious choice brings one to aspire to lead, with the focus always on the growth and well-being of people and the communities to which they belong.
There have always been questions about implementing this leadership style in a hyper-competitive and global business environment. Servant-leadership success stories are many, as over 70% of the Fortune 500 practice servant-leadership. This form of leadership has multiple benefits, but some challenges do exist, so let’s dive in.
Key Principles of Servant Leadership
Servant leadership is built on several core principles:
- Listening: Servant leaders prioritize active listening to understand the needs and perspectives of their team members.
- Empathy: They strive to understand and relate to others’ experiences and emotions.
- Healing: Servant leaders help foster emotional and psychological well-being within their teams.
- Awareness: They cultivate self-awareness and situational awareness to make informed decisions.
- Persuasion: They aim to build consensus through persuasion and influence rather than using authority.
- Conceptualization: Servant leaders balance day-to-day operations with long-term vision and planning.
- Foresight: They learn from past experiences to anticipate future outcomes and challenges.
- Stewardship: Servant leaders view their role as stewards, responsible for the well-being of their organization and its people.
- Commitment to growth: They dedicate themselves to each team member’s personal and professional development.
- Building community: Servant leaders foster community and shared purpose within their organizations.
Comparing Servant Leadership to Other Leadership Styles
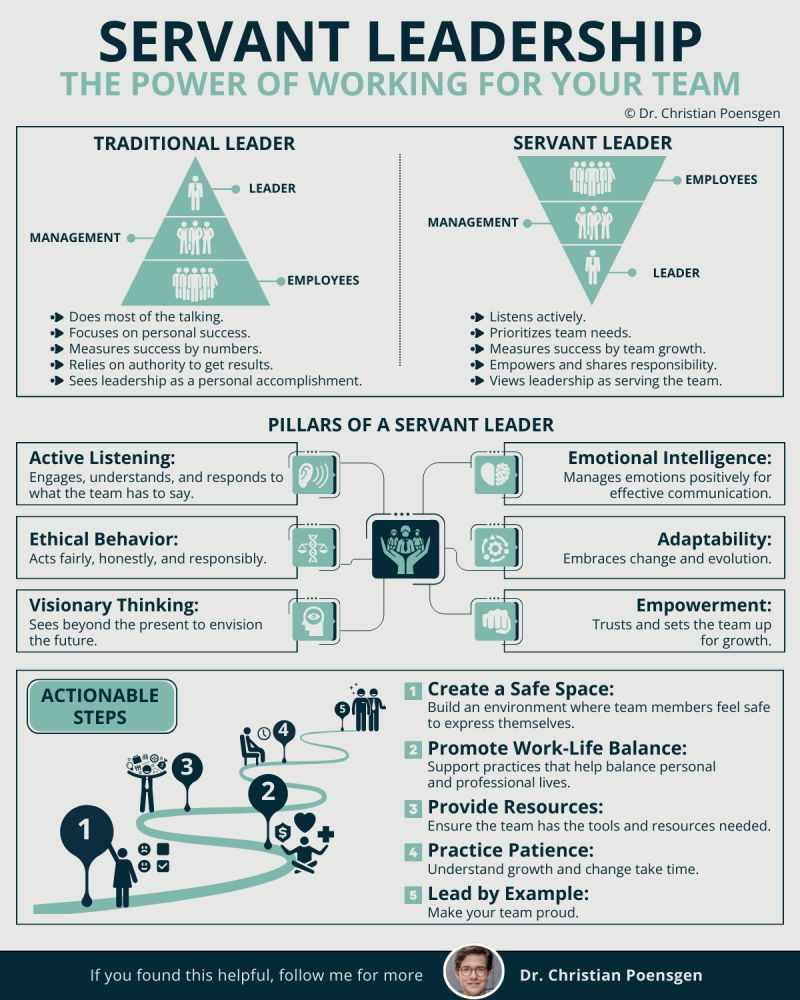
To fully appreciate servant-leadership’s unique aspects, it’s helpful to compare it with other popular leadership styles. At its core, servant-leadership puts the team at the top of the pyramid. Almost all leadership models do the exact opposite. This comparison highlights its distinctive features and provides context for when and where it might be most effective.
70% of the Fortune 500 practice servant-leadership
Servant Leadership vs. Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leadership is characterized by individual control over all decisions, with little input from team members.
Key differences:
- Decision-making: Servant leaders encourage input and collaboration, while autocratic leaders make unilateral decisions.
- Focus: Servant leaders prioritize team development, whereas autocratic leaders focus on task completion and control.
- Communication: Servant leadership promotes open, two-way communication, while autocratic leadership often involves one-way, top-down directives.
Autocratic leadership can be effective in crises requiring quick decisions, but servant leadership generally fosters better long-term employee satisfaction and engagement.
Servant Leadership vs. Transformational Leadership
Transformational leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating followers to exceed their self-interests for the organization’s benefit.
Similarities:
- Both styles emphasize vision and employee growth.
- Both aim to bring about positive change in individuals and organizations.

Differences:
- Primary focus: Servant leaders prioritize the needs of their followers first, while transformational leaders focus on organizational goals and inspiring others to achieve them.
- Approach to influence: Servant leaders lead by example and support, while transformational leaders use charisma and inspiration to motivate.
Servant Leadership vs. Democratic Leadership
Democratic leadership involves group participation in decision-making processes.
Similarities:
- Both styles value input from team members.
- Both promote a sense of ownership among employees.
Differences:
- Decision-making: While democratic leaders ultimately make decisions based on group input, servant leaders may empower team members to make decisions themselves.
- Focus: Democratic leadership centers on equal participation, while servant leadership emphasizes individual growth and well-being.

Servant Leadership vs. Laissez-faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership provides minimal guidance to team members, allowing them significant autonomy.
Similarities:
- Both styles trust employees to manage their responsibilities.
- Both can promote creativity and innovation.
Differences:
- Level of involvement: Servant leaders actively support and develop their teams, while laissez-faire leaders adopt a hands-off approach.
- Guidance: Servant leaders offer direction and mentorship, whereas laissez-faire leaders provide little oversight.
Servant Leadership vs. Situational Leadership
Situational leadership adapts leadership style based on the maturity and competence of team members.
Similarities:
- Both recognize that different individuals or situations require different approaches.
- Both emphasize flexibility in the leadership approach.
Differences:
- Core philosophy: Servant leadership consistently focuses on serving others, while situational leadership varies its approach more dramatically based on circumstances.
- Development approach: Servant leaders consistently invest in team member growth, whereas situational leaders may vary their developmental support based on the individual’s current competence level.
Organizational and Market Contextual is Important
The effectiveness of any leadership style, including servant leadership, can depend on various factors:
- The Individual Leader: Servant Leadership requires a high level of self-awareness of the specific organization or team leader.
- Organizational culture: Servant leadership may thrive in cultures that value collaboration and employee empowerment but might face resistance in highly hierarchical or traditional environments.
- Industry dynamics: Fast-paced industries with rapid decision-making needs might find aspects of servant leadership challenging to implement fully.
- Team composition: Teams with highly skilled, self-motivated individuals may benefit more from servant leadership than those requiring close supervision.
- Organizational goals: Companies focusing on long-term sustainability and employee retention may find servant leadership particularly effective.
- External pressures: In times of crisis or significant market pressures, more directive leadership styles might work alongside servant leadership principles.

CEOs Embracing Servant Leadership
Many successful CEOs have adopted servant leadership principles in their management approach:
- Bill Marriott: (Executive Chairman and Former CEO): Servant leadership has been a core tenant in Marriot’s leadership style and is imbedded in the company’s core values. They put people first and believe that if you take care of the associates, they will take care of the customers.
- Howard Schultz (former CEO of Starbucks): Schultz built Starbucks’ culture around serving others, including employees, customers, and communities.
- Herb Kelleher (co-founder and former CEO of Southwest Airlines): Kelleher famously prioritized employees, believing that happy employees would lead to satisfied customers and business success. His famous quote, “I have always believed that the best leader is the best server,” rings true today.
- John Mackey (Founder of Whole Foods): Mackey is a strong proponent of servant leadership and believes that instead of thinking of business as a battlefield or a jungle, it should be thought of as a community.
- Ken Blanchard (author and management expert): While not the CEO of a large corporation, Blanchard has been instrumental in promoting and teaching servant leadership principles to organizations worldwide.
Pros and Cons of Servant Leadership
Like any leadership model, servant leadership has its advantages and potential drawbacks:
The Advantages of Servant Leadership:
- Increased employee engagement and satisfaction
- Improved team collaboration and communication
- Enhanced trust between leaders and team members
- Higher retention rates due to a positive work environment
- Stronger organizational culture built on shared values
The Downside of Servant Leadership
- Can be time-consuming to implement, especially in large organizations
- May be perceived as “soft” or lacking authority in some corporate cultures
- Requires a significant mindset shift for leaders accustomed to traditional hierarchies
- Can be challenging to balance serving others with making tough business decisions
- May not be suitable for crises requiring quick, decisive action

Organizational Structures Best Suited for Servant Leadership
While servant leadership can be beneficial in various settings, certain organizational structures are particularly well-suited for this approach:
- Flat organizations: Companies with fewer hierarchical levels allow for more direct communication and collaboration between leaders and team members.
- Team-based structures: Organizations that rely heavily on cross-functional teams can benefit from servant leaders who facilitate cooperation and empower team members.
- Non-profit organizations: The service-oriented nature of non-profits aligns well with servant leadership principles.
- Healthcare institutions: Patient-centered care models often incorporate servant leadership to improve patient outcomes and staff satisfaction.
- Educational institutions: Schools and universities can benefit from servant leaders prioritizing student and faculty development.
- Start-ups and small businesses: The close-knit nature of small businesses and startups allows for more personal relationships between leaders and team members.
- Customer service-oriented companies: Businesses prioritizing customer satisfaction can leverage servant leadership to create a service culture at all levels.
5 Benefits of Implementing Servant Leadership
Increased Innovation and Creativity
Serving leadership can foster innovation by empowering employees and creating a safe environment for idea-sharing. When team members feel valued and supported, they’re more likely to take risks and propose creative solutions to challenges. Studies have shown that psychological safety boosts creativity.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Servant leaders model a service-oriented mindset that often translates to better customer experiences. When employees feel cared for and empowered, they’re more likely to extend that same care to customers.

Enhanced Organizational Agility
Servant leadership promotes open communication and decentralized decision-making, allowing organizations to respond more quickly to market changes and customer needs.
Stronger Succession Planning
By focusing on the growth and development of team members, servant leadership naturally creates a pipeline of future leaders within the organization.
Positive Impact on Society
Servant leadership creates a sense of purpose among teams and individuals. Servant-led organizations often extend their focus beyond profit to consider their impact on employees, customers, and the broader community. This contributes to a more sustainable and socially responsible business model.

Implementing Servant Leadership in Your Organization
Transitioning to a servant leadership model requires commitment and patience. Here are some steps to begin the process:
- Start with self-reflection: Leaders must examine their beliefs and behaviors and identify areas for improvement to serve their teams better.
- Communicate the vision: Clearly articulate the principles of servant leadership and how they align with the organization’s goals and values.
- Lead by example: Demonstrate servant leadership in daily interactions with team members and stakeholders.
- Invest in training: Provide development programs focusing on servant leadership principles and skills.
- Create feedback mechanisms: Establish systems for team members to provide honest feedback on leadership practices.
- Celebrate servant leadership in action: Recognize and reward behaviors that exemplify servant leadership principles.
- Be patient: Cultural change takes time. Allow for a gradual shift in mindset and practices throughout the organization.
Challenges and Considerations
While servant-leadership offers numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge potential challenges:
- Resistance to change: Some team members may be skeptical of a leadership approach that differs from traditional models.
- Balancing service with authority: Leaders must balance serving others and maintaining necessary authority and decision-making power.
- Measuring impact: The effects of servant leadership can be challenging to quantify, making it difficult to demonstrate ROI to stakeholders.
- Avoiding burnout: Servant leaders must be mindful of their well-being while focusing on serving others.
- Adapting to different contexts: Servant leadership principles may need to be adjusted based on cultural and organizational contexts.
A Management Style for an Uncertain Future
Servant leadership represents a powerful shift in how we conceptualize effective leadership. Admittedly, it’s not for every leader and requires a high degree of self-awareness by the individual. Additionally, it can become dissonant with the cutthroat environments of global business. However, by prioritizing the growth and well-being of team members, servant leaders can create more engaged, innovative, and purpose-driven organizations. While it may require significant effort to implement, the potential benefits to employees, customers, and the broader community make servant leadership a compelling model for modern organizations.
The upheaval in the global workforce, the unpredictable behavior of GenZ workers, and the explosion of AI will continue to shape employer-employee models for the next decade. As such, more effective leadership models will be needed to maintain organizational cohesion and effectively compete in the global marketplace. As we navigate increasingly complex business environments, servant leadership principles offer a framework for building resilient, adaptable, and human-centered organizations. By embracing this approach, leaders can drive business success and contribute to developing a more compassionate and sustainable corporate landscape.
To learn more about solutions and our partnerships for growth, reach out to the team at ClearSky 2100 Ventures.
Disclosure: At ClearSky 2100, our portfolio partly consists of affiliate partnerships. We may earn a small commission from buying links on our site at no cost to you.