Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a distant concept. It’s here, firmly entrenched in society, transforming our workplaces and redefining the future of work. Particularly, the prevalence of AI agents is on the rise, with many viewing them as the precursor to artificial general intelligence. They automate routine tasks and augment human capabilities, leading to a more efficient and flexible workforce. However, the rise of AI agents is not without its controversy. It’s reshaping job roles, changing the skills required, and even influencing the structure of the workforce.
In this article, we delve into these complexities. We’ll explore the implications of agentic AI on the future of work, offering insights into the integration of AI in remote work and current developments in AI regulation. We’ll also delve into the importance of upskilling and reskilling, use cases for AI agents in action across the care economy, and a review of AI agent development platforms such as agent.ai. Be sure to follow us on LinkedIn and join us as we navigate the delicate landscape of AI agents and the future of work. Let’s jump into it.
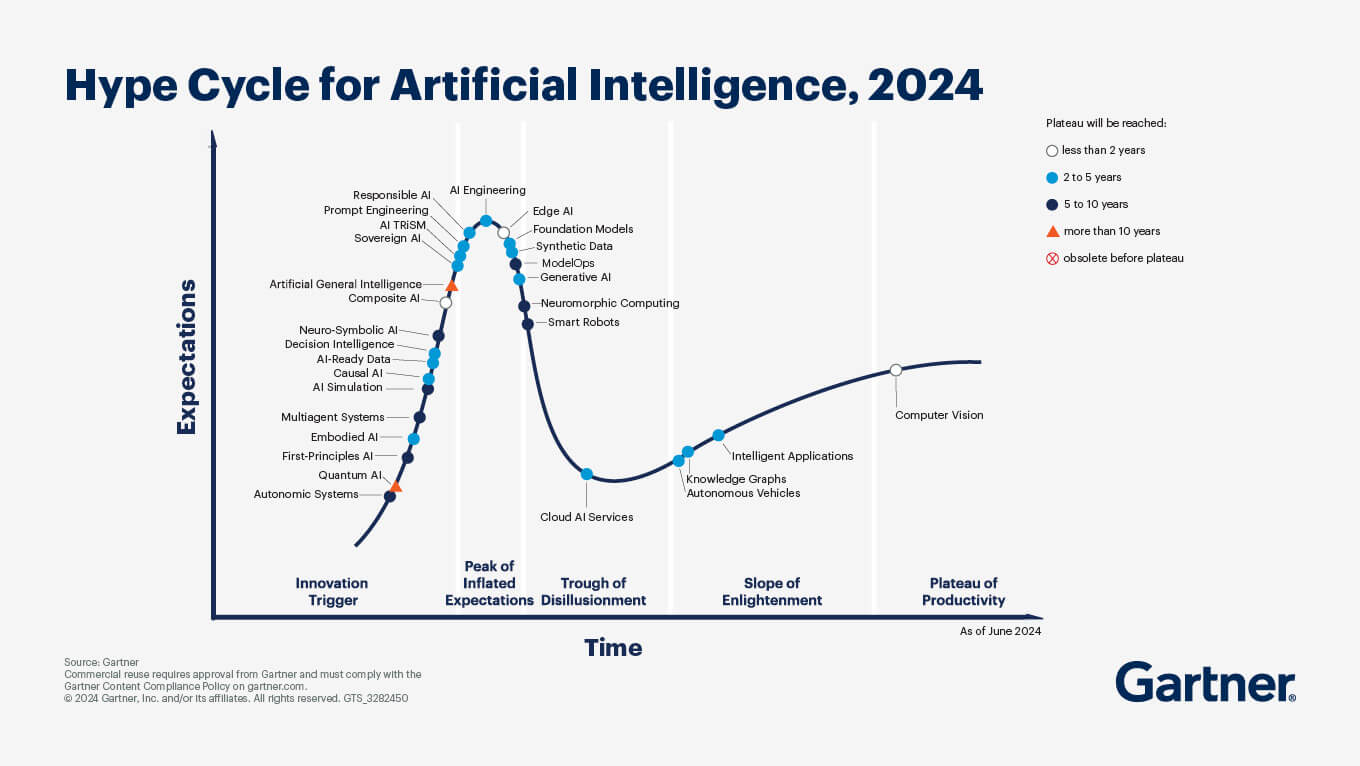
Agentic AI: A Precursor to AGI
Agentic AI is a system that uses sophisticated reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously solve complex multi-step problems. AI agents can be considered precursors to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), but with important distinctions and caveats. There are several reasons why this is the case.
Why AI Agents Are Precursors to AGI
- Task Automation and Problem Solving: AI agents are increasingly capable of handling complex, multi-step tasks autonomously. This involves decision-making, learning from data, and adjusting to new inputs, which are foundational capabilities required for AGI.
- Context Awareness: Advanced AI agents are capable of interpreting and responding to context, which bridges the gap between narrow AI (focused on specific tasks) and AGI (capable of understanding and performing a wide range of tasks).
- Integration of Learning and Action: Some AI agents can learn from experiences and apply those learnings to different scenarios, a key attribute of AGI. For example, reinforcement learning agents adapt their strategies based on feedback, emulating certain aspects of human problem-solving.
- Scalable Architectures: Modern AI architectures, such as those behind large language models (LLMs), are designed with scalability in mind. They can process vast amounts of data, learn complex patterns, and perform tasks in ways that edge closer to general intelligence.

Limitations of AI Agents
- Narrow Domain Expertise: Most AI agents excel in specific domains but struggle when asked to generalize knowledge across unrelated fields—an essential feature of AGI.
- Lack of True Understanding: AI agents currently operate based on patterns and probabilities without true comprehension or reasoning. AGI would need to understand the underlying meaning of concepts deeply.
- Dependence on Training Data: AI agents are heavily dependent on their training data. They cannot independently acquire the broad, diverse, and nuanced knowledge AGI would require.
- Lack of Self-Awareness: AGI is often envisioned as possessing self-awareness and the ability to reflect on its own thinking, which current AI agents lack.
- Ethical and Emotional Intelligence: Current AI lacks the ethical reasoning and emotional understanding needed for AGI-level interactions and decisions.
Stepping Stones to AGI
Depsite the hype cycle underway in AI, agentic AI is a critical component on the pathway toward AGI. The evolution of Ai agents demonstrates progress in areas like contextual reasoning, multi-modal learning (e.g., combining text, images, and sound), and adaptability. However, significant breakthroughs in areas like causal reasoning, unsupervised learning, and consciousness are required for the leap to AGI. This goal may be at least a decade away.
The Rise of AI Agents in the Workplace
AI agents are now integral to the modern workplace. Their presence is felt across various sectors, from technology to finance. These agents handle tasks that once demanded human input, streamlining operations and reducing time spent on mundane activities. Today, over 45% of companies use AI as digital personal assistants or for customer relationship management.
Deloitte predicts that in 2025, 25% of companies that use gen AI will launch agentic AI pilots or proofs of concept, growing to 50% in 2027
The adoption of AI agents is not uniform across industries. Sectors such as tech, finance, and healthcare lead the way. These industries leverage AI agents for roles including data analysis, customer service, and even creative processes. The following industries are rapidly adopting AI agents:
- Financial Services: Fraud detection, risk management, customer service automation.
- Retail and E-commerce: Customer experience and operations management
- Healthcare: Improving diagnostic accuracy, improving patient outcomes, and operational efficiency
- Legal Services: Contract analysis, e-discovery, and predictive analytics
- Media and Telecommunications: Churn predictive analytics, manuscript evaluation, personalizing content creation
AI agents excel in task automation. They enhance productivity by performing repetitive tasks at a faster rate and with fewer errors than humans. This frees up human workers to focus on tasks that require creativity and critical thinking. An onboarding AI agent built by Mckinsey was able to reduce lead time by 90% and administrative work by 30%
Key Areas Where AI Agents are Transforming the Workplace
- Automating routine administrative tasks
- Assisting in data analysis and decision-making processes
- Enhancing customer interaction through chatbots and virtual assistants
- Contributing to product development and design with predictive modeling
Despite these advancements, AI brings challenges as well as opportunities. Concerns about job displacement and economic inequality are real. In economies heavily dependent on call centers, such as the Philippines, the use of AI agents could result in the displacement of 300,000 jobs. However, prospects for new roles and industries driven by AI innovation counterbalance these concerns. As businesses embrace these agents, the need for strategic planning and ethical considerations becomes crucial to balance technological advances with social impacts.

AI Agent Development Platforms
Global companies like Microsoft and Salesforce have developed platforms that empower users to create AI agents with minimal or no coding requirements, thereby democratizing AI development.
No-Code and Low-Code AI Agent Building Platforms
- Microsoft’s Copilot Studio: This low-code platform allows users to build and customize AI agents, known as copilots, to automate various tasks. It integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 and other business applications, enhancing productivity by enabling users to create AI solutions without extensive programming knowledge.
- Salesforce’s Agentforce: Agentforce is a low-code platform that enables businesses to build and deploy autonomous AI agents tailored to roles such as customer service or sales. These agents integrate with the Salesforce ecosystem, automating tasks and improving operational efficiency. The platform provides tools like Flows, Apex, and MuleSoft APIs for easy customization.
- Meta AI Studio: Meta’s AI Studio is a no-code platform designed to enable users to create personalized AI agents seamlessly. Powered by Meta’s Llama 3.1 language model, the platform simplifies AI agent development to be deployed across the Meta ecosystem.
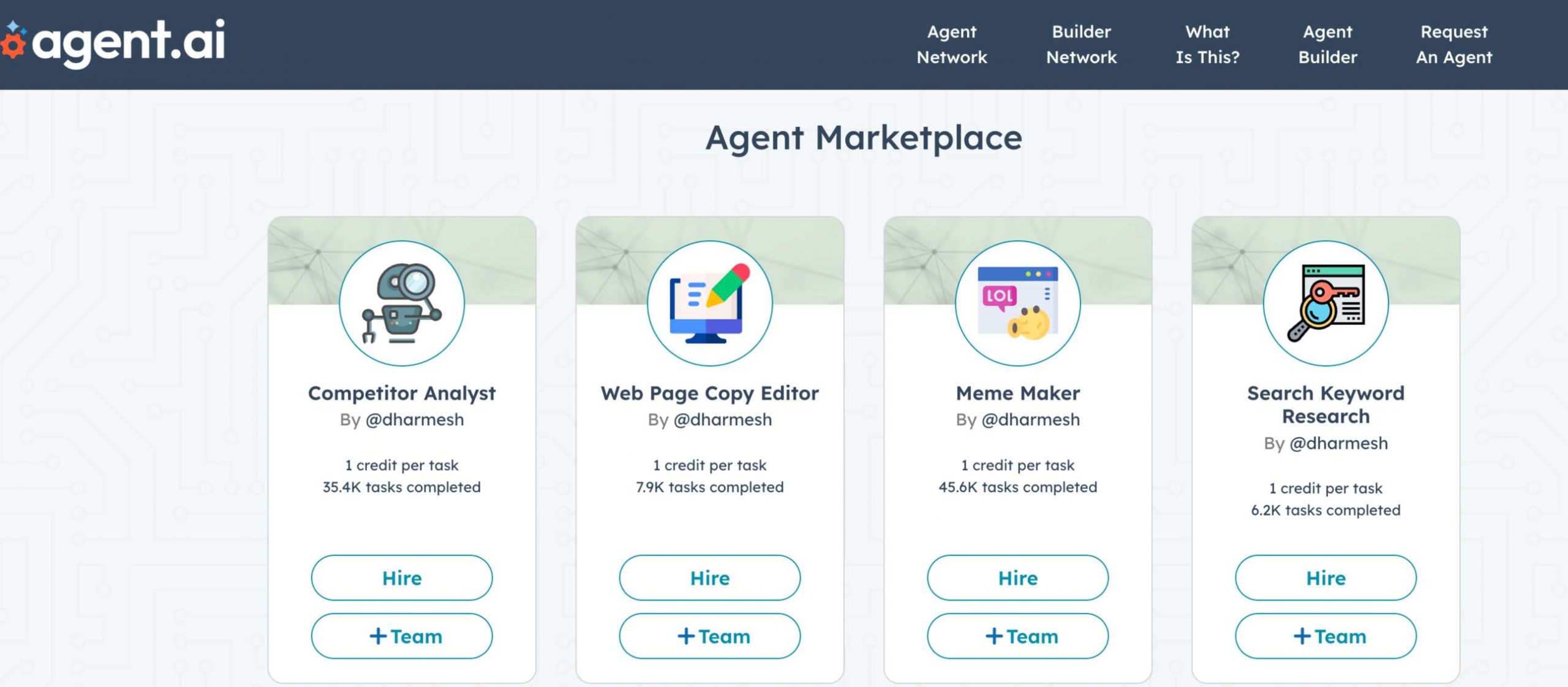
Overview of agent.ai
Agent.ai is a professional network and marketplace to build, train, and hire professional AI agents. The platform has been developed under the leadership of Dharmesh Shah, co-founder and CTO of HubSpot. It enables users to discover, connect with, and utilize AI agents capable of performing a diverse array of tasks, enhancing productivity across various domains.
The “Only” Professional Network for AI Agents
The primary mission of agent.ai is to democratize access to AI capabilities by providing a centralized platform where users can engage with AI agents to accomplish tasks efficiently. By fostering a network of AI agents, agent.ai aims to integrate AI seamlessly into daily workflows, thereby augmenting human capabilities and streamlining operations.
Key Advantages of Agent.ai
- User-Friendly Interface: Agent.ai offers an intuitive platform that allows users to easily find and interact with AI agents without requiring extensive technical expertise.
- Diverse Agent Capabilities: The platform hosts a variety of AI agents capable of tasks ranging from company research and competitive analysis to website optimization and content summarization, catering to a wide spectrum of user needs.
- Scalability and Collaboration: Agent.ai is leveraging one of HubSpot’s best-in-class capabilities—community building—to open its platform to external developers, enabling the addition of new agents and fostering a collaborative ecosystem that continually expands the platform’s capabilities.
Agent.ai offers a user-friendly platform connecting users with versatile AI agents to enhance productivity. As agentic capabilities continue to gain popularity in AI development, we anticipate the emergence of numerous new players. However, we believe agent.ai is off to a fantastic start, providing a holistic approach to creating AI Agent teams and building community to further innovation.
Global Regulation of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The regulation of artificial intelligence is a developing field, with governments and organizations worldwide taking steps to address the ethical, legal, and societal implications of AI. Below is a summary of the current regulatory landscape:
United States
- Sector-Specific Approach: The U.S. has fragmented AI regulation, with existing laws targeting specific industries like healthcare, finance, and transportation. In the US Congress several key pieces of AI legislation are under consideration. These include the Artificial Intelligence Civil Rights Act of 2024 and the AIxBio Defense Sandbox Act, among many others.
- AI Bill of Rights: The White House introduced a blueprint outlining principles for the safe and ethical use of AI, focusing on user privacy and algorithmic fairness.
- FTC Oversight: The Federal Trade Commission, through its Operation AI Comply, has begun addressing issues like misleading AI claims and discriminatory algorithms under consumer protection laws.
European Union
- AI Act: The EU is leading global AI regulation with its AI Act, which came into force on August 1, 2024 The law classifies AI systems by risk level (unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal). High-risk systems face strict requirements for transparency, accountability, and safety.
- GDPR Impact: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) influences AI development by ensuring data privacy and the right to explanation for decisions made by AI systems.
China
- Proactive Regulations: China has implemented regulations on algorithms, requiring transparency and accountability for recommendation systems.
- Ethics and Security: New rules emphasize AI’s ethical use and national security concerns, aligning with the government’s broader technological governance.
Global Initiatives
- OECD Principles on AI: Adopted by over 40 countries, these guidelines promote AI that is inclusive, sustainable, and respects human rights and democratic values.
- UNESCO’s AI Ethics Framework: Aims to create a global ethical standard for AI development and deployment.
Key Challenges to Global Regulation of AI
Regulators worldwide are falling behind as the pace of AI adoption accelerates. As they grapple with policy challenges, key themes are emerging as they legislate a regulatory framework.
- Harmonization: Diverse approaches to AI regulation create challenges for multinational companies seeking compliance.
- Bias and Fairness: Ensuring algorithms are non-discriminatory remains a top concern.
- Innovation vs. Control: Striking a balance between fostering innovation and implementing safeguards against misuse.
The regulatory landscape for AI continues to evolve, with significant advancements expected as policymakers address the rapid growth and societal impacts of AI technologies.

AI in Remote Work: A New Paradigm
In today’s global economy, one can work from almost anywhere. By 2030, there will be an expected 92 million digital jobs, up from 72 million in 2024. Remote work is possible for many of these jobs. Therefore, the incorporation of AI in remote work is transforming the way we accomplish tasks. It provides flexibility and efficiency, enabling employees to perform effectively from diverse locations. AI tools play a pivotal role in managing remote teams and coordinating tasks.
Communication is crucial in remote work, and AI enhances this aspect significantly. Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools aid clear and effective communication between teams. AI-driven platforms like monday.com are instrumental in improving workflows by maintaining seamless interactions across teams. AI also supports productivity in remote settings. Tools powered by AI help manage workloads, set deadlines, and track progress. mondayAI recently introduced AI into its solution architecture. mondayAI brings additional efficiency to teams in optimizing workflows. Key areas of improvement for teams include sentiment analysis, categorization, and information extraction, etc.
AI also supports productivity in remote settings. Tools powered by AI can help manage workloads, set deadlines, and track progress. Automation of routine tasks frees workers to engage more deeply with complex challenges that require human intuition.
Benefits of AI in Remote Work
- Improved communication with NLP tools
- Enhanced task management and scheduling
- Increased efficiency through automation
- Greater flexibility for employees and employers
As companies navigate the future of work, embracing AI in remote settings is essential. This shift calls for ongoing adaptation to integrate AI smoothly into existing workflows, ensuring that both employees and employers reap the full benefits of this technological evolution.
Human-AI Collaboration: The New Frontier
The collaboration between humans and AI agents is transforming industries, creating opportunities for innovation and efficiency. This partnership leverages the strengths of both human intuition and AI’s analytical power. The result is a synergy that enhances productivity and opens new pathways for business growth. While on the surface the benefits seem apparent, results remain mixed.
In sectors like healthcare, human-AI collaboration is revolutionizing patient care. AI can process vast amounts of medical data quickly, while human professionals provide the necessary empathy and judgment for patient interactions. This teamwork leads to better diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
The creative industries, too, are benefiting from human-AI collaboration. Artists and designers utilize AI tools to explore novel art forms and expand the limits of their creativity. AI can generate ideas and designs, while human creativity refines and brings them to life.
According to a recent study, human-AI collaboration revealed that on average, combined systems (human-AI) underperform compared to the best of humans or AI alone.
Benefits of Human-AI Collaboration
- Enhances decision-making with data-driven insights
- Expands creative possibilities in arts and design
- Improves precision and efficiency in manufacturing
- Increases scalability in customer service operations
In manufacturing, AI optimizes production processes, predicting maintenance needs and improving quality control. Meanwhile, human workers handle complex problem-solving and adjustments, ensuring smooth operations. This blend of capabilities leads to enhanced production efficiency and reduced costs.
As AI technologies continue to evolve, the potential for human-AI collaboration will only grow. Businesses that embrace this dynamic are likely to stay ahead of the curve, tapping into the full potential of both human and artificial intelligence for a prosperous future.

Key Focus Areas for Human-AI Partnerships
- Automated scheduling and reminders
- Data-driven performance insights
- Task prioritization based on algorithms
Collaboration tools powered by AI enhance team dynamics by facilitating seamless communication. AI enables the integration of diverse tools into a unified platform, simplifying collaboration across different departments and locations.
Upskilling and Reskilling in an AI-Driven Economy
The rapid adoption of AI technologies is reshaping job requirements across industries. Workers need new skills to thrive in this evolving landscape. Therefore, upskilling and reskilling have become critical strategies for both employees and employers. According to a recent report from LinkedIn, over 75% of knowledge workers are using AI at the workplace.
Organizations face the challenge of preparing their workforce for AI integration. Continuous learning initiatives are essential. They equip employees with skills such as data analysis, machine learning basics, and digital literacy. This ensures that companies remain competitive and can harness AI’s full potential.
For individuals, staying relevant means embracing lifelong learning. The onus is on workers to seek out opportunities for skill enhancement, often through online courses or vocational training programs. This proactive approach can mitigate the risk of job displacement by AI.
Key Skills for an AI-driven Economy:
- Data analysis and interpretation
- Basic coding and algorithm understanding
- Critical thinking and problem-solving
- Effective communication and collaboration
By focusing on upskilling and reskilling, society can turn AI-induced disruption into opportunities for growth. As AI technologies continue to reshape industries, a skilled workforce is indispensable in ensuring a balanced and progressive economy.

Agentic AI in the Global Care Economy
As AI agents take root across industries, one useful case study to understand the potential is the care economy. Digital transformation is revolutionizing the global care economy by integrating advanced technologies into traditional sectors. The care economy faces a $11 trillion workforce crisis. The adoption of agentic AI solutions is enhancing healthcare delivery, from patient monitoring to personalized treatment plans and improvement of long-term care models. This transformation is crucial for meeting the growing demand for efficient care services.
AI agents are playing a significant role in automating administrative tasks within the care economy. Key use cases for agentic AI in the global care economy include:
- Scheduling appointments
- Managing billing systems
- Claims Processing
- Care Coordination
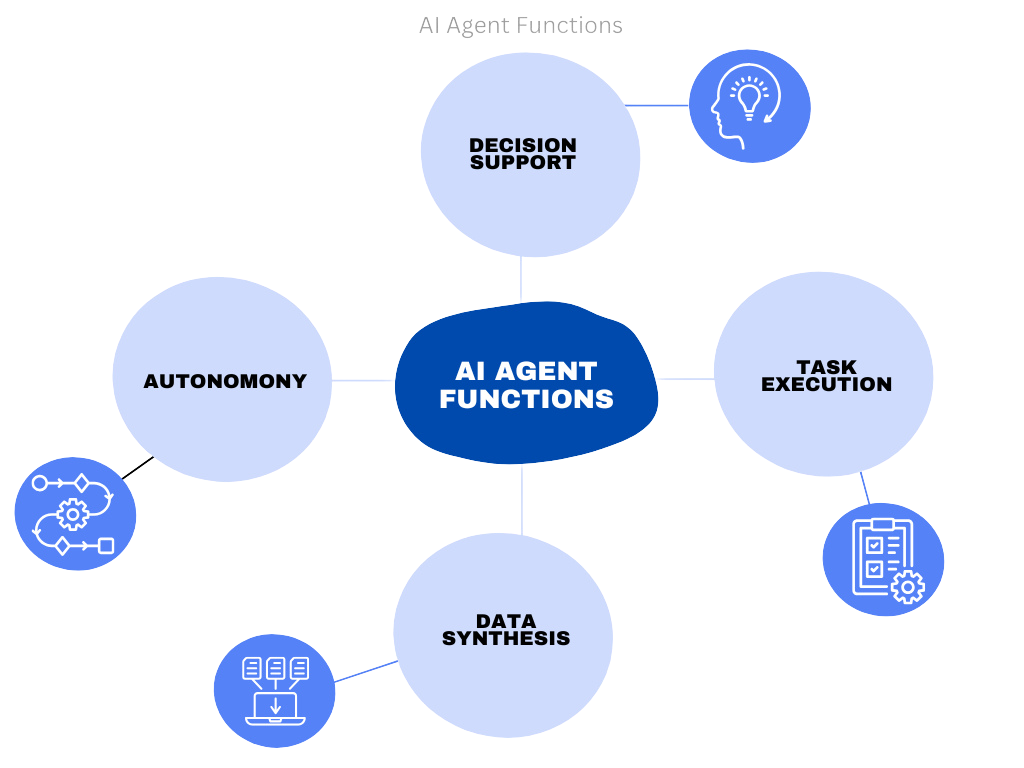
AI Agent Functions in the Care Economy
Image Credit: Productive Edge
These benefits will allow us to focus more on patient care. This shift not only increases productivity but also improves the quality of services provided.
The global population continues to rapidly age. While agentic AI cannot replace the last mile of elder care, its ability to streamline the value chain of services easing the workforce crisis will be transformative.
Making AI Agents Work For a Prosperous Future
Finally, AI’s potential to enhance productivity and innovation is reshaping the future of work. To fully capitalize on these opportunities, it is crucial to embrace AI integration across various sectors. AI agents have the ability to transform the global workplace. While fears exist, opportunities sound. As societies grapple with the challenges and opportunities presented by AI, the most effective course of action is to embrace technological advancements but prepare workers for a transformative future. By doing so, businesses, policymakers, and workers can navigate the challenges and reap the benefits of AI advancements.
Embracing AI involves strategic workforce planning, investment in upskilling, and a commitment to ethical AI practices. AI agent development platforms such as agent.ai and others offer both enthusiasts and workers opportunities to harness AI to become more productive and explore new areas of growth. This approach will not only mitigate the risks associated with automation but also foster a prosperous work environment. Collaboration between humans and AI will ultimately drive economic growth and societal progress, paving the way for a promising future.
Disclosure: At ClearSky 2100, our portfolio partly consists of affiliate partnerships. We may earn a small commission from buying links on our site at no cost to you.